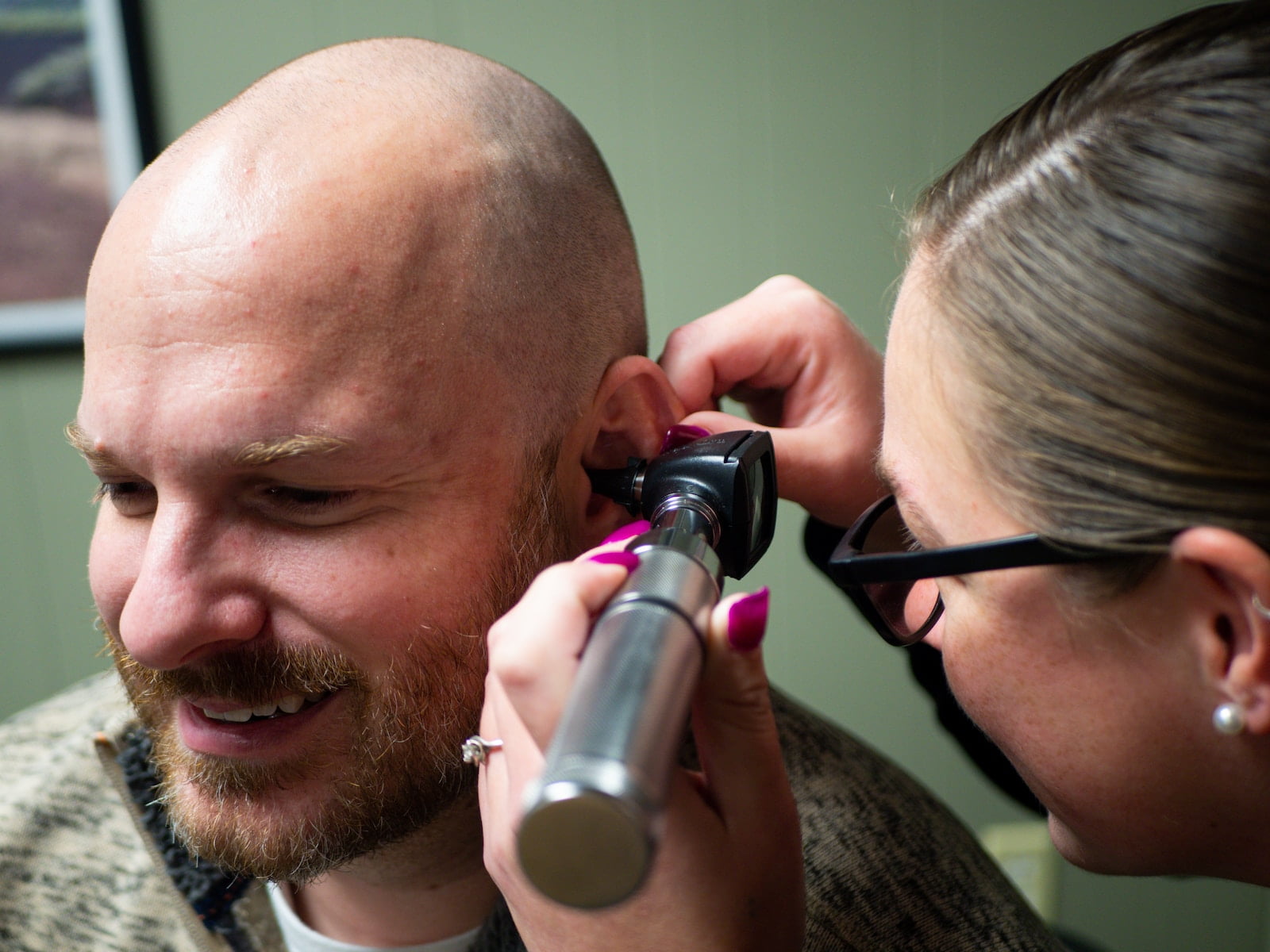
Ear wax buildup is a common problem that affects a significant number of individuals around the world. While some people may resort to home remedies or over-the-counter solutions, others seek professional help for manual instrument ear wax removal. This procedure is performed by trained audiologist who possess the necessary skills and knowledge to safely remove ear wax using specialised instruments. In recent years, the demand for professionals in this field has increased, leading to advanced job opportunities in manual instrument ear wax removal. In this article, we will explore the various roles and responsibilities of these professionals, the required qualifications, and the potential career prospects.
Professionals specialising in manual instrument ear wax removal play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing complications associated with excessive ear wax buildup. Their primary responsibility is too safely and effectively remove ear wax using manual instruments such as curettes, forceps, or suction devices. They must possess a thorough understanding of the anatomy of the ear and be able to identify any abnormalities or signs of infection.
In addition to removing ear wax, these professionals are responsible for providing education and counselling to patients regarding ear care and hygiene practices. They should be able to answer questions, address concerns, and offer guidance on preventive measures. Moreover, they may also collaborate with other healthcare providers, such as ENT’s in complex cases or when further examination or treatment is required.
To expand on the content under “Roles and Responsibilities,” we can further discuss the following points:
To pursue a career in manual instrument ear wax removal, individuals typically need to meet certain qualifications. These requirements may vary depending on the country or region, but generally include:
Audiologist who are trained in manual instrument ear wax removal will have a strong foundation of knowledge of medical terminology to effectively communicate with other healthcare providers and patients and understanding the anatomy of the ear which is crucial for safe and effective ear wax removal.
Certification programs provide professionals with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform manual instrument ear wax removal safely and effectively. These programs typically cover topics such as the different instruments used in the procedure, abnormalities that can be found in the ear, proper techniques for ear wax removal, and infection prevention protocols. By obtaining certification, audiologist have demonstrate their competence and commitment to providing high-quality care to their patients.
The increasing awareness of the importance of ear health and the demand for safe and effective ear wax removal methods have contributed to the growth of advanced job opportunities in manual instrument ear wax removal. Here are some potential career paths for professionals in this field:
In conclusion, manual instrument ear wax removal presents advanced job opportunities for professionals in the field of ear health. By possessing the necessary qualifications and skills, individuals can pursue a fulfilling career in this specialised area with becoming audiologists or nurses who specialise in ear wax removal. Whether as ear wax removal specialists, audiologists, or otolaryngologist assistants, these professionals play a vital role in maintaining ear health and providing essential services to individuals experiencing ear wax buildup.
On many occasions after providing a full hearing assessment I get asked the question “can…
Microsuction is a safe and effective method for removing earwax and debris from the ear…
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a substance that is naturally produced by our…
Ear wax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ear canal to protect…
Cleaning our ears is an important part of our personal hygiene routine. It not only…
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the ear canal to…
This website uses cookies.