By the Numbers: Unpacking Efficacy Studies on Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
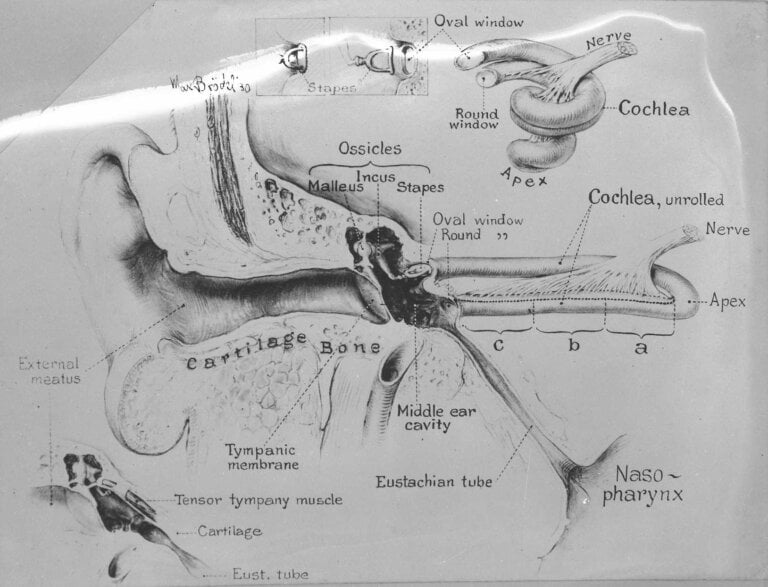
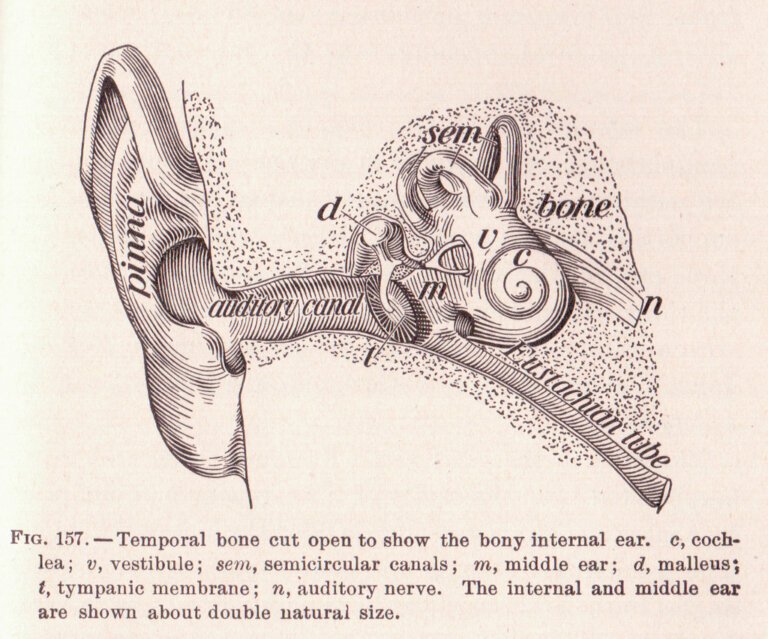
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a naturally occurring substance produced by glands in the ear canal. While it serves the purpose of protecting the ear canal and preventing infections, excessive buildup of ear wax can lead to discomfort, impaired hearing, and other complications. To address this issue, manual instrument ear wax removal techniques have been widely employed by healthcare professionals. In this article, we will delve into the efficacy studies conducted on manual instrument ear wax removal, exploring the numbers and findings that shed light on its effectiveness.
Understanding Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Manual instrument ear wax removal involves the use of tools such as curettes, suction devices, forceps, or loops to physically remove ear wax from the ear canal. This technique is typically performed by healthcare professionals, including audiologists, ear, nose, and throat specialists, or general practitioners. By manually manipulating the instruments, ear wax can be safely and effectively removed, providing relief to individuals experiencing symptoms associated with excessive wax buildup.
The Importance of Efficacy Studies
Efficacy studies play a crucial role in assessing the effectiveness of manual instrument ear wax removal techniques. These studies provide valuable insights into the success rates, safety profiles, and patient satisfaction associated with the procedure. By analysing the data obtained from these studies, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding the appropriate course of treatment for their patients.
Efficacy studies help us understand the outcomes of manual instrument ear wax removal techniques. They provide quantitative data on the success rates, which can range from 60% to 98%. Factors such as the severity of the wax buildup, the expertise of the healthcare professional, and the patient’s individual characteristics can influence the success rate. By considering these factors, Audiologists can better predict the effectiveness of the procedure for each patient.
In addition to success rates, efficacy studies also assess the safety profiles of manual instrument ear wax removal. When performed by Audiologists, the procedure is generally considered safe. However, there may be slight risks associated with the process, such as minor trauma to the ear canal or discomfort. Adverse events are rare but can be minimised by seeking professional assistance. These studies provide valuable information to healthcare professionals to ensure a safe and successful procedure.
Moreover, patient satisfaction is a significant aspect of evaluating the efficacy of manual instrument ear wax removal. Studies consistently show high levels of patient satisfaction with this technique. Patients experience immediate relief following the procedure, and their hearing is restored to normal. Improved overall ear health contributes to their satisfaction. By considering patient satisfaction, Audiologists can gauge the effectiveness of the procedure from the patient’s perspective.
Examining Efficacy Studies on Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Several efficacy studies have been conducted to evaluate the success and safety of manual instrument ear wax removal techniques. Let’s explore some of the key findings from these studies:
- Success Rates: Research indicates that manual instrument ear wax removal is generally effective, with success rates ranging from 60% to 98%. These rates may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the wax buildup, the expertise of the healthcare professional, and the patient’s individual characteristics.
- Success rates can be influenced by the severity of the wax buildup. In cases where the wax accumulation is minimal, the success rate tends to be higher. However, for severe or impacted wax, the success rate may be lower.
- The expertise of the Audiologists performing the procedure also plays a crucial role. Experienced professionals are more likely to achieve higher success rates due to their skill and familiarity with the instruments.
- Patient characteristics, such as the size and shape of the ear canal, can also affect the success rate. Individuals with narrower or more challenging ear canals may have a lower success rate compared to those with more accessible canals.
- Safety Profiles: When performed by trained professionals, manual instrument ear wax removal is considered safe. While there may be slight risks associated with the procedure, such as minor trauma to the ear canal or discomfort during the process, adverse events are rare. It is crucial to seek professional assistance to minimise the chances of complications and ensure a safe and successful procedure.
- Minor trauma to the ear canal can occur due to the nature of the procedure. However, this is usually temporary and heals without long-term consequences.
- Discomfort during the process is a common experience reported by some patients. It is important to note that this discomfort is usually minimal and transient.
- Adverse events, such as infections or severe injuries, are rare when the procedure is performed by trained professionals following proper protocols.
- Patient Satisfaction: Studies have consistently shown high levels of patient satisfaction with manual instrument ear wax removal. This can be attributed to the immediate relief experienced by patients following the procedure, as well as the restoration of normal hearing and improved overall ear health.
- Immediate relief from discomfort and symptoms associated with excessive ear wax buildup contributes significantly to patient satisfaction. The removal of the wax allows individuals to experience improved hearing and relief from any related issues, enhancing their overall quality of life.
- The restoration of normal hearing is a primary goal of the procedure, and when achieved, it greatly contributes to patient satisfaction. Clearer hearing allows individuals to engage more effectively in conversations, enjoy music, and carry out daily activities without hindrance.
- Comparative Studies: Some studies have compared manual instrument ear wax removal to other techniques, such as irrigation or the use of ear drops. While these alternatives may be effective in certain cases, manual instrument removal often proves to be more successful, especially for impacted or hard-to-reach wax.
- Comparative studies highlight the advantages of manual instrument ear wax removal over other techniques. This technique is particularly beneficial for cases where the wax is impacted or difficult to reach.
- Irrigation, which involves flushing the ear canal with water or a saline solution, can be effective for some individuals. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with a history of ear infections or perforated eardrums.
- The use of ear drops to soften the wax before removal is another alternative. While this method can be effective for mild cases, it may not be as successful for more severe wax buildup.
Best Practices for Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
To maximise the efficacy of manual instrument ear wax removal, healthcare professionals follow a set of best practices. These practices include:
- Proper Assessment: Conducting a thorough examination of the ear canal and assessing the severity of the wax buildup before proceeding with the removal procedure.
- A comprehensive assessment of the ear canal is essential to determine the most appropriate approach for wax removal. Healthcare professionals carefully evaluate the extent of the wax buildup and consider any underlying factors that may affect the procedure.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks or discomfort to ensure informed consent and cooperation.
- Informing patients about the procedure is crucial to manage their expectations and alleviate any concerns they may have. By explaining the benefits, risks, and potential discomfort associated with the process, Audiologists can obtain informed consent and ensure patient cooperation during the procedure.
- Sterilisation and Hygiene: Adhering to strict sterilisation protocols to minimise the risk of infections or cross-contamination during the procedure.
- Maintaining a sterile environment is of utmost importance to prevent infections and ensure patient safety. Healthcare professionals follow strict sterilisation protocols to minimise the risk of cross-contamination and maintain a clean and hygienic setting.
- Gentle Technique: Employing a gentle and cautious approach while manipulating the instruments to avoid potential damage to the ear canal or eardrum.
- Gentle manipulation of the instruments is essential to prevent any harm to the delicate structures of the ear. Healthcare professionals exercise caution and expertise to ensure a safe and effective procedure.
- Follow-up Care: Providing appropriate post-procedure care instructions, including the use of prescribed ear drops or cautionary measures to prevent further wax accumulation.
- After the procedure, healthcare professionals provide patients with detailed instructions on post-procedure care. This may include the use of prescribed ear drops to prevent future wax buildup or cautionary measures to maintain ear hygiene.
Conclusion
Manual instrument ear wax removal is a widely used technique that offers effective relief from the discomfort and symptoms associated with excessive ear wax buildup. Efficacy studies have consistently shown high success rates, safety profiles, and patient satisfaction with this procedure. By following best practices and seeking professional assistance, individuals experiencing ear wax-related issues can benefit from this procedure and restore their hearing and overall ear health.