Determining Who Can Benefit from Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Last Updated on 3rd May 2024 by Admin
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. While ear wax serves a protective function, it can sometimes accumulate and cause discomfort or hearing problems. When this happens, manual instrument ear wax removal can be a safe and effective option.
What is Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal?
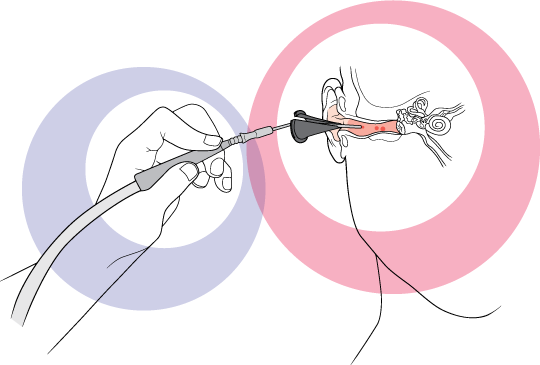
Manual instrument ear wax removal, also known as ear syringing or ear irrigation, is a procedure that involves the use of specialized instruments to remove excessive ear wax from the ear canal. It is typically performed by trained healthcare professionals such as audiologists, ear, nose, and throat specialists, or general practitioners.
Who Can Benefit from Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal?
Manual instrument ear wax removal can be beneficial for individuals who experience the following symptoms:
- Ear Discomfort: Excessive ear wax can cause a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the ear. Manual removal can provide relief by eliminating the blockage. In some cases, the buildup of ear wax can even lead to ear infections or inflammation, making manual removal essential for alleviating the discomfort.
- Hearing Loss: Buildup of ear wax can lead to temporary hearing loss or muffled sounds. By removing the excess wax, hearing can be restored. This can be especially important for individuals who rely on their hearing for work or daily activities.
- Earache: In some cases, impacted ear wax can cause pain or an earache. Manual removal can alleviate the discomfort and resolve the underlying issue. It is important to note that persistent earaches should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any other potential causes.
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus refers to the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ears. While ear wax may not be the primary cause of tinnitus, removing the wax can sometimes improve symptoms. This is particularly true if the tinnitus is caused by the wax blocking external sounds from reaching the inner ear.
- Itching or Odor: Excessive ear wax can lead to itching or an unpleasant odor in the ear. Manual removal can address these issues and improve overall ear hygiene. Itching and odor can be signs of an underlying infection, so it is important to have a healthcare professional evaluate the situation.
It is important to note that not everyone with ear wax buildup requires manual instrument removal. For some individuals, the excess wax may naturally migrate out of the ear canal without intervention. However, if you experience persistent symptoms or are unsure about the best course of action, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional.
The Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal Process
The process of manual instrument ear wax removal typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment: A healthcare professional will begin by examining your ear canal using an otoscope. This allows them to assess the extent of the wax buildup and determine the most appropriate removal method. They will also check for any signs of infection or inflammation.
- Preparation: Before the removal procedure, the professional may use an otological solution to soften the ear wax. This helps facilitate its removal and minimizes discomfort. The solution may contain ingredients such as hydrogen peroxide or saline, which help break down the wax and make it easier to remove.
- Instrument Insertion: Using specialized instruments such as curettes, forceps, or suction devices, the healthcare professional will carefully insert them into the ear canal to remove the ear wax. They will use gentle movements to avoid causing any injury to the ear. The choice of instrument depends on the individual’s unique situation and the healthcare professional’s preference and expertise.
- Post-Procedure Care: After the removal, the healthcare professional may recommend ear drops or provide guidance on how to maintain proper ear hygiene to prevent future wax buildup. This may include using over-the-counter ear drops or a homemade solution of vinegar and water to help keep the ears clean and prevent excess wax from accumulating.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While manual instrument ear wax removal is generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential risks and considerations to keep in mind:
- Perforation Risk: There is a small risk of accidentally perforating the eardrum during the removal process. This risk is minimized when the procedure is performed by trained professionals who have experience and expertise in ear wax removal techniques. It is important to choose a healthcare professional who is qualified and skilled in performing this procedure.
- Infection Risk: If the ear canal is already infected or inflamed, manual removal may not be advised as it can potentially lead to further complications. In such cases, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. They may prescribe antibiotics or other medications to treat the infection before considering ear wax removal.
- Bleeding or Discomfort: Some individuals may experience mild discomfort or slight bleeding during or after the removal procedure. These symptoms typically resolve on their own and are often temporary. However, if the discomfort or bleeding persists or worsens, it is important to seek medical attention.
- Alternative Methods: In some cases, manual instrument removal may not be suitable or effective. Alternative methods such as ear drops, ear irrigation, or microsuction may be recommended instead. These methods can be less invasive and may be more appropriate for individuals with sensitive ears or certain medical conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, manual instrument ear wax removal can provide relief for individuals experiencing ear discomfort, hearing loss, earaches, tinnitus, itching, or odor caused by excessive ear wax. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine if this procedure is necessary and appropriate for your specific situation. The healthcare professional will be able to assess your symptoms, evaluate the condition of your ear canal, and recommend the most suitable treatment option. By following proper techniques and considering potential risks, manual instrument ear wax removal can effectively improve ear health and restore normal hearing.
FAQ
1. What is manual instrument ear wax removal?
Manual instrument ear wax removal, also known as ear syringing or ear irrigation, is a procedure that involves the use of specialized instruments to remove excessive ear wax from the ear canal. It is typically performed by trained healthcare professionals such as audiologists, ear, nose, and throat specialists, or general practitioners.
2. Who can benefit from manual instrument ear wax removal?
Manual instrument ear wax removal can be beneficial for individuals who experience the following symptoms:
- Ear discomfort
- Hearing loss
- Earache
- Tinnitus
- Itching or odor
3. What is the process of manual instrument ear wax removal?
The process of manual instrument ear wax removal typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment
- Preparation
- Instrument Insertion
- Post-Procedure Care
4. What are the potential risks and considerations of manual instrument ear wax removal?
While manual instrument ear wax removal is generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential risks and considerations to keep in mind:
- Perforation risk
- Infection risk
- Bleeding or discomfort
- Alternative methods