Understanding the Differences between Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Last Updated on 25th April 2024 by Admin
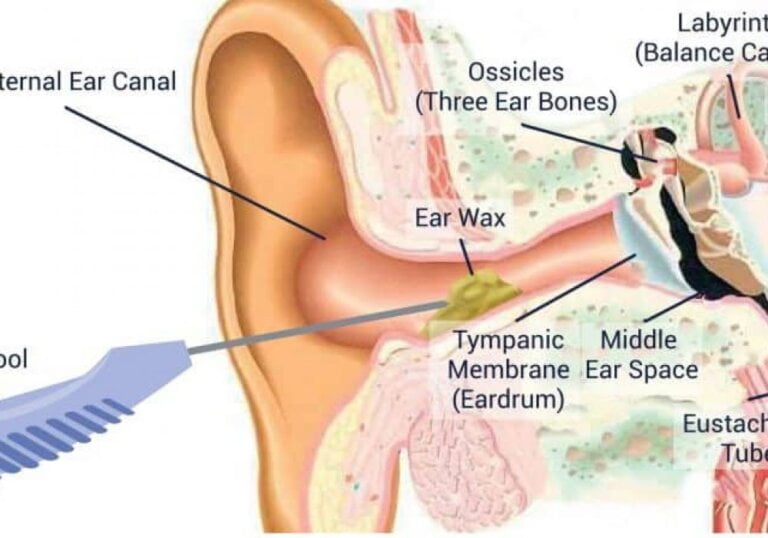
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, is a waxy substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. While it serves a protective purpose, excessive ear wax can lead to hearing loss, earache and other discomfort. To address this issue, manual instrument ear wax removal techniques are commonly used. In this article, we will delve into the various methods and their differences to better understand the options available for effective ear wax removal.
1. Introduction to Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
Manual instrument ear wax removal is a process that involves the use of specialised tools, such as curettes, loops, and forceps, to extract accumulated ear wax from the ear canal. This method provides a more precise and controlled approach compared to other methods like ear drops or irrigation. It is typically carried out by healthcare professionals, such as ear nose and throat specialists or audiologists, who have the necessary expertise and training in the procedure.
Manual instrument ear wax removal allows healthcare professionals to directly visualise the ear canal under magnification and target the specific areas where the wax is accumulated. This targeted approach ensures that the wax is effectively removed without causing any harm or discomfort to the patient. Additionally, healthcare professionals can adjust the pressure and angle of the instruments according to the patient’s needs, ensuring a safe and comfortable experience.
2. Different Techniques of Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
2.1 Curettage
Curettage is a widely used technique for ear wax removal. It involves the use of a small, curved instrument called a curette, which is gently inserted into the ear canal to scrape off the ear wax. The process requires skill and caution to ensure the wax is effectively removed without causing any harm or discomfort to the patient.
Curettage is particularly suitable for removing dry or hardened wax that may be adhered to the ear canal walls. The curved shape of the curette allows it to reach the nooks and crannies of the ear canal, ensuring thorough removal. The healthcare professional performing the procedure will carefully navigate the curette through the ear canal, using light pressure to scrape off the wax.
2.2 Looping
Looping, also known as wire loop extraction, is another common method used in manual instrument ear wax removal. A fine wire loop is carefully manoeuvred around the ear canal to gently scoop out the wax. This technique is often employed when the ear wax is relatively soft and pliable.
Looping allows for delicate and controlled removal, minimising the risk of injury to the ear canal. The loop is designed to be flexible, allowing the healthcare professional to navigate it smoothly through the ear canal. By gently scooping out the wax, looping ensures that the entire mass is removed, reducing the chances of residual wax causing further discomfort or hearing loss.
2.3 Forceps
Forceps, similar to the ones used in surgical procedures, can also be utilised in manual instrument ear wax removal. This technique involves the use of specially designed forceps to grasp and extract the ear wax. It is often preferred for larger and more stubborn wax build-ups that may not be easily removed by other methods.
Forceps provide a firm grip, allowing for effective removal while minimising discomfort to the patient. The healthcare professional will carefully insert the forceps into the ear canal and grasp the wax, gently pulling it out. The use of forceps requires precision and expertise to avoid any injury to the delicate structures of the ear canal.
3. Factors to Consider in Manual Instrument Ear Wax Removal
When opting for manual instrument ear wax removal, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure safe and effective results:
3.1 Severity of Ear Wax Build-up
The severity of the ear wax build-up plays a crucial role in determining the most appropriate technique for removal. For mild cases, curettage or looping may suffice, while more extensive or impacted wax may require the use of forceps. It is important for healthcare professionals to assess the condition and choose the technique that best suits the individual patient’s needs.
3.2 Individual Sensitivity
Each individual’s ear canal is unique, and some people may have more sensitive or narrow ear canals. In such cases, the healthcare professional performing the procedure must exercise extra caution to prevent injury or discomfort. They should be aware of the patient’s sensitivity and adjust their technique accordingly, ensuring a gentle and comfortable experience.
3.3 Expertise of the Healthcare Professional
The expertise and experience of the healthcare professional performing the ear wax removal are of utmost importance. It is essential to seek assistance from a qualified specialist, such as an ear nose and throat specialist or audiologist, who has the necessary training and skills to perform the procedure safely and effectively. A skilled professional will be able to assess the condition, choose the appropriate technique, and minimise the risk of complications.
4. Precautions and Post-procedure Care
Proper precautions and post-procedure care are necessary to minimise the risk of complications and ensure optimal results. Here are some general guidelines to follow:
- Avoid Self-Removal: Attempting to remove ear wax at home using cotton buds or other objects can push the wax deeper into the ear canal, potentially causing damage or impaction. It is important to avoid inserting anything into the ear canal and leave the removal to healthcare professionals.
- Seek Professional Help: If you experience persistent symptoms like hearing loss, ear pain, or a feeling of fullness in the ear, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They will be able to evaluate the condition of your ear and recommend the most suitable method of ear wax removal.
- Follow Aftercare Instructions: After the manual instrument ear wax removal procedure, follow any instructions provided by the healthcare professional regarding ear hygiene and any prescribed ear drops or ointments. These instructions are important for maintaining ear health and preventing further wax build-up or complications.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular ear check-ups can help identify any potential issues early on and prevent the accumulation of excessive ear wax. It is advisable to schedule periodic appointments with a healthcare professional specialising in ear care to ensure ongoing monitoring and maintenance of ear health.
Conclusion
Manual instrument ear wax removal techniques, such as curettage, looping, and forceps, offer effective solutions for addressing ear wax build-up. Each technique has its own advantages and is chosen based on the severity of the condition and individual factors. To ensure safe and successful removal, it is crucial to consult a qualified healthcare professional who specialises in ear care. Remember, maintaining proper ear hygiene and seeking professional assistance when needed are key to preventing complications and maintaining good ear health.